Ebola virus disease outbreak

Recovery toolkit: Supporting countries to achieve health service resilience
10 May 2016 -- The recovery toolkit is online library of guidance resources to support countries in the reactivation of health services which may have suffered as a result of an emergency, such as the Ebola outbreak. These services include ongoing programmes such as immunization, maternal and child health services, infection prevention and control.

Beyond Ebola, keeping patients and health workers safe
5 May 2016 -- The isolation and transit room near the entrance to Coleah Medical Centre is one of 12 that WHO built in the past year at under-resourced health facilities in Guinea with inadequate triage structures. Eight more are under construction, to be used for any highly infectious diseases, including Ebola.

Liberia and Guinea discharge final Ebola patients in latest flare-up and begin 42 days of heightened surveillance
2 May 2016 -- Liberia’s Ministry of Health, WHO and partners held a ceremony at the Ebola treatment facility in Monrovia to celebrate the recovery and discharge of a 2-year-old boy, the final patient in a latest flare-up in Liberia. His 5-year-old brother recovered a week earlier.
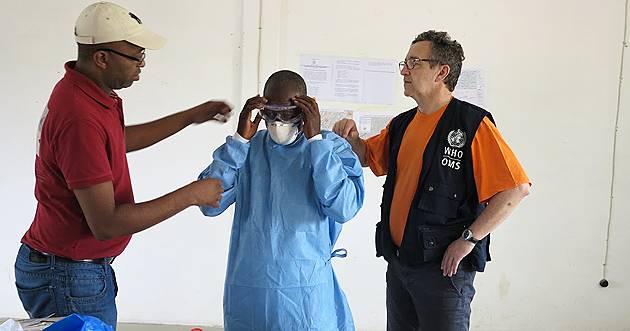
The role of training in the West Africa Ebola response
20 April 2016 -- The magnitude of the 2014-2015 West Africa Ebola outbreak combined with a dearth of local and international expertise in tackling the disease necessitated training on a mass scale. Over the duration of the epidemic, WHO and partners trained more than 8,000 health professionals from over 80 nations, including the Ebola-affected countries. To better understand the impact of the trainings, WHO commissioned a review, which was conducted by an independent, external body.

Guidance on clinical care of Ebola survivors
Ebola virus RNA has been detected at low levels in breast milk up to 16 months after onset of symptoms. More evidence is needed to know the precise duration and infectivity of Ebola virus persistence in breast milk. EVD survivors who are lactating may wish to have their breast milk tested for Ebola virus by RT-PCR. Women who do not know the status of their breast milk or who were tested and for whom no Ebola virus RNA was detected should continue breastfeeding.
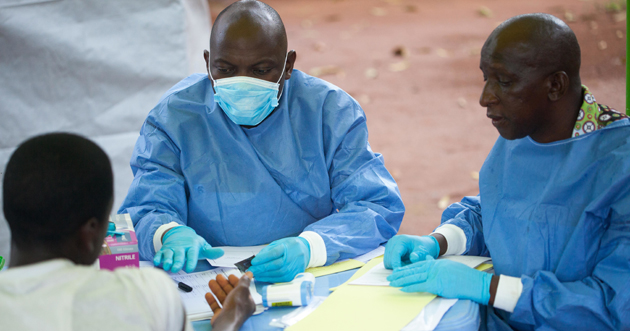
Looking, hopefully, towards an Ebola-free future
15 April 2016 -- WHO, partners and affected countries are stepping up planning for how to use an Ebola vaccine in response to an outbreak. The Ebola outbreak that struck Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone in 2014 prompted the search, on an exceptionally accelerated schedule, for a vaccine to prevent the disease. Although there has been more than one promising candidate, the vesicular stomatitis virus-ebola virus (VSV-EBOV) vaccine was selected.

Liberia and Guinea step up coordination to stem new cases of Ebola
7 April 2016 -- WHO and Ministry of Health teams in Guinea and Liberia have established epidemiological links between new Ebola cases in Liberia and a current flare-up of Ebola in neighbouring Guinea following intensified case investigations and contact tracing.

Emergency response to Ebola flare underway in Liberia. Case investigation widens to Guinea
4 April 2016 -- WHO and Ministry of Health teams in Liberia and Guinea are investigating the origins of transmission in Liberia’s latest flare-up after learning that a woman who died from Ebola in Liberia last week had recently travelled from Guinea with her three young children. Liberian health authorities quickly reactivated the country’s emergency response mechanisms and with support from key partners.
fact buffet
Situation report
28,616A total of 28,616 Ebola cases have been reported in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone, with 11,310 deaths.
Ebola Situation Report, 26 MayDashboard
10,000Today, there are over 10,000 survivors of Ebola virus disease.
For more: Ebola dashboard of achievementsPhase 3
3 objectivesTo interrupt all remaining chains of Ebola transmission. To respond to the consequences of residual risks. To work on health systems recovery.
For more: Read the report on Phase 3Technical guidance
Latest updates
-
Beyond Ebola, keeping patients and health workers safe in Guinea
5 May 2016 -
Liberia and Guinea discharge final Ebola patients in latest flare-up and begin 42 days of heightened surveillance
2 May 2016 -
The role of training in the West Africa Ebola response
21 April 2016 -
Looking, hopefully, towards an Ebola-free future
15 April 2016 -
Liberia and Guinea step up coordination to stem new cases of Ebola
7 April 2016
Ebola survivors
Health systems recovery
Feature stories
-
Beyond Ebola, keeping patients and health workers safe
5 May 2016 -
Liberia and Guinea discharge final Ebola patients in latest flare-up and begin 42 days of heightened surveillance
2 May 2016 -
Looking, hopefully, towards an Ebola-free future
15 April 2016
Stories by country
Health workers
Ebola situation reports
The situation reports include summary of the situation, tables, maps, and data on number of cases, deaths in Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone and other affected countries. As of May 2016, the situation report is issued in pdf format only.
- Situation reports archive - pdf version
- Recent situation reports
- Situation reports archive - html version
Data, statistics, maps
WHO statements
Ebola training
Over the duration of the epidemic, WHO and partners trained more than 8,000 health professionals from over 80 nations. The training topics included:
Partners
Social media
Tweets about #ebola from:whoResearch and development
WHO has convened a coalition of experts to develop the blueprint and a platform for accelerated research and development, which will be presented to Member States at the World Health Assembly in May 2016.
Preparedness
WHO has transitioned its emergency preparedness support to a broader range of risks, and extended activities to other countries, including Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Chad, Democratic Republic of Congo, Malawi, Tanzania, and Uganda.






